EXTENSIVE PRE-CLINICAL VALIDATION STUDY
![]()
RETROSPECTIVE ANALYSIS OF 250 PLASMA SAMPLES
collected from pregnant women who underwent traditional NIPT (low resolution) and targeted non-invasive prenatal screening for a group of 79 genetic diseases (targeted SGD NIPT).
![]()
TEST RESULTS CONFIRMED USING INVASIVE PRENATAL DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES
(amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling).
![]()
PRENATALGENOME DEMONSTRATED HIGHER SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY COMPARED TO TRADITIONAL NIPTS.
HIGHER SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY COMPARED TO TRADITIONAL NIPT IN DETECTING CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES
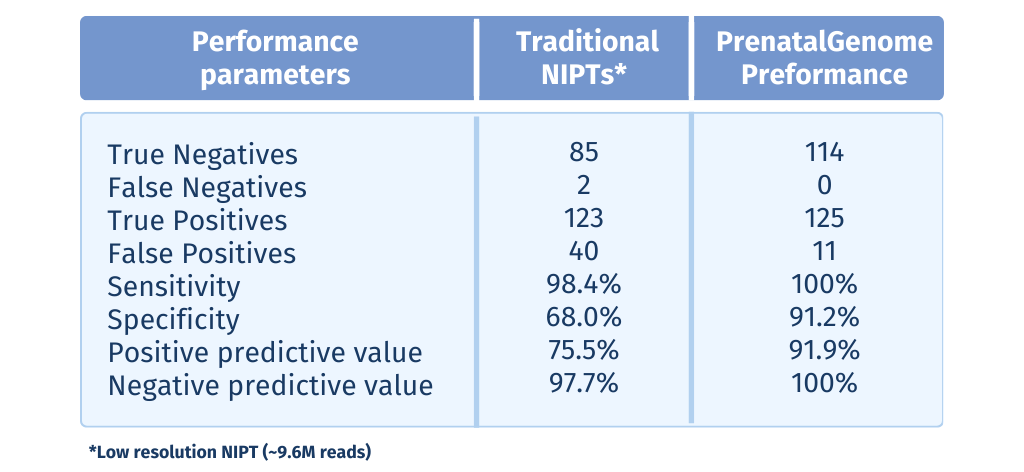
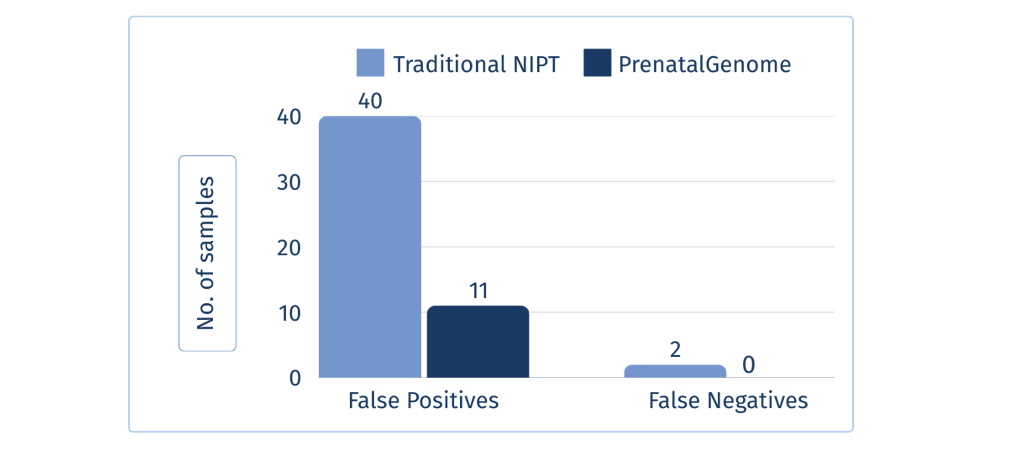
A pre-clinical validation study assessed the performance of PrenatalGenome in detecting chromosomalabnormalities, including common and rare aneuploidies, as well as structural chromosomal alterations (e.g.deletions/duplications and microdeletion/microduplication syndromes). This study included 250 plasmasamples from pregnant women previously tested with low-resolution traditional NIPT, with results confirmedby invasive prenatal diagnostic techniques such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling. PrenatalGenome demonstrated superior sensitivity and specificity, significantly reducing false positives (40 vs.11) and false negatives (2 vs. 0) compared to traditional NIPT. Overall, the test achieved 100% sensitivity (versus98.4% for traditional NIPT, p < 0.001) and significantly improved specificity at 91.2% (compared to 68.0% fortraditional NIPT, p < 0.001).*
HIGH SENSITIVITY AND SPECIFICITY IN DETECTING SEVERE GENETIC DISEASES IN THE FETUS
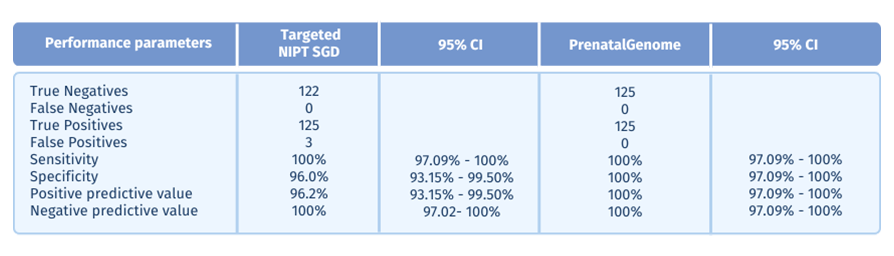
PrenatalGenome ’s ability to identify mutations responsible for severe genetic diseases, both inherited and denovo, was confirmed through a retrospective analysis of 250 plasma samples. These samples were obtainedfrom pregnant women who had previously undergone non-invasive prenatal screening for a panel of 79 geneticdiseases (targeted SGD NIPT). Results were confirmed using invasive prenatal diagnostic techniques. PrenatalGenome achieved 100% sensitivity (95% CI: 97.1–100%) and 100% specificity (95% CI: 97.1–100%) indetecting pathogenic de novo and paternally inherited mutations.*


 Italiano
Italiano English
English