
THE MOST ADVANCED AND COMPREHENSIVE NIPT
Traditional NIPT tests are limited by their low resolution to detecting fetal aneuploidies and structural chromosomal abnormalities. PrenatalGenome marks a significant technological advancement over conventional NIPT. In addition to identifying common and rare fetal aneuploidies, deletions, duplications, and microdeletion/ microduplication syndromes, it screens for approximately 7,000 clinically recognized severe genetic diseases , both inherited and de novo. This is achieved through high-resolution sequencing of the entire protein-coding fetal genome (exome), covering over 20,000 genes. The PrenatalGenome Plus screening option also includes a carrier screening test for both parents to assess the carrier status of gene mutations related to ~7000 genetic diseases.
24
CHROMOSOMES
ANEUPLOIDY SCREENING
Screening for common and rare fetal aneuploidies, segmental deletions and duplication § across the whole fetal genome, providing karyotype-level insight.
§Segmental detetions and duplications >7 Mb
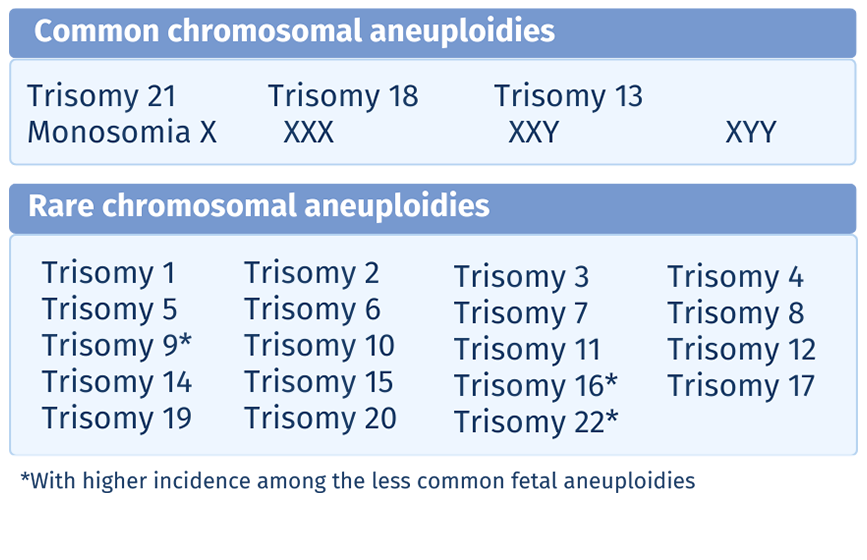
> 130
MICRODELETION / MICRODUPLICATION SYNDROMES
as low as a 1 Mb
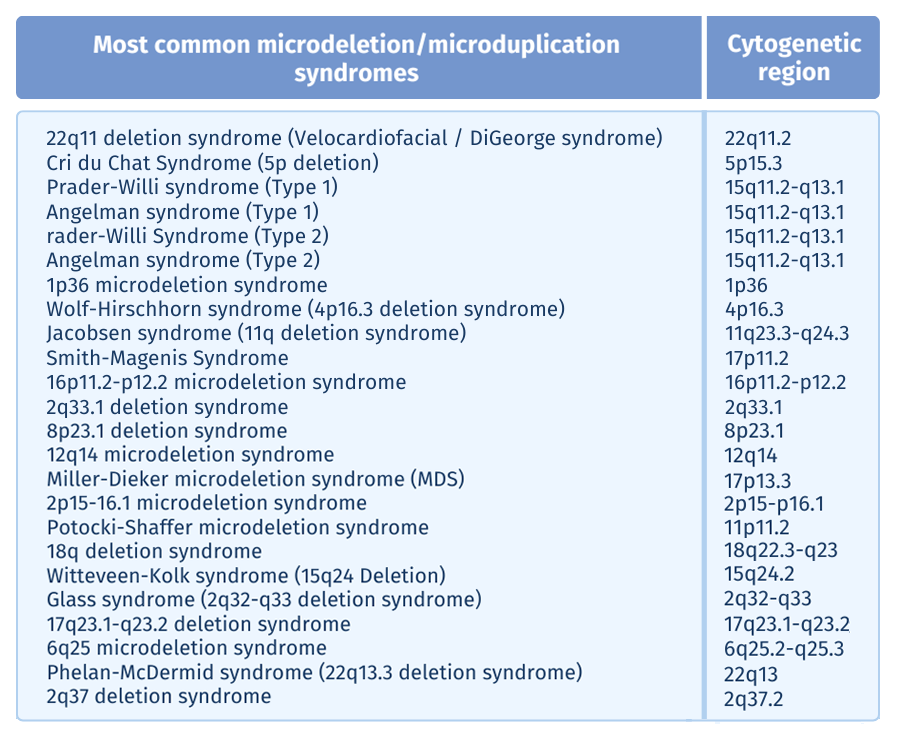
View Complete List
∼ 20.000
GENES
Over 20,000 protein-coding genes make up the exome. Mutations inapproximately 5,000 of these genes are associated with about 7,000 genetic diseases with known phenotypes.
View Complete List
∼ 7.000
GENETIC DISORDERS
By analyzing the entire coding fetal genome (exome), the PrenatalGenome test enables screening of thousands of clinically recognized genetic diseases in the fetus.
View Complete List
GENETIC DISEASES OF DE NOVO
De novo genetic diseases arise from random mutations in the fetal exome that are absent in the parents,making them undetectable through pre-conception carrier screening tests. These mutations can lead toconditions such as skeletal dysplasias, congenital heart defects, multiple congenital anomalies, autism,epilepsy, and/or intellectual disabilities. Many of these conditions are often not detectable by ultrasound, especially in early pregnancy. PrenatalGenome effectively detects de novo genetic diseases, which have a cumulative incidence ofapproximately 1 in 600, increasing to 1 in 300 for conditions linked to developmental delays.¹⁻²
INHERITED GENETIC DISEASES
Inherited genetic diseases result from mutations in the fetal exome passed down from carrier parents, often unaware of their status. PrenatalGenome enables the detection of mutations responsible for thousands of inherited genetic conditions.
The analysis of the fetal exome increases the detection rate by approximately 30% compared to other prenataldiagnostic techniques. It is especially recommended for pregnancies involving fetal structural anomalies.³⁻⁴
2. McRae J, et aL Prevalence and architecture of de novo mutatians in develapmental disarders. Nature 2017: 542:433-438.
3. Van den Veyver IB, et al. International Society for Prenatal Diagnosis updated position statement on the use of genome-wide sequencing for prenatal diagnosis. Prenat Diagn. 2022;42:796-803.
4. Mellis R, et al.. Diagnostic yield of exome sequencing for prenatal diagnosis of fetal structural anomalies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prenat Diagn. 2022;42:662-685.


 Italiano
Italiano English
English